Introduction
I’m sure you’ve already heard about the Interface Definition Language (IDL) if you’ve ever worked with RPC. Yes, if you want to make RPC calls, you can use DCOM by Microsoft, CORBA…Although the technologies are different but they have the same thing: the IDL must be defined first. Then, a tool can compile and generate the IDL to server/client side stubs and skeletons for you to add more details to implement your RPC methods.
OpenClovis IDL is not an exception but the difference is that you don’t have to write your own IDL, instead, we have the IDE helping you define your methods, datatypes… and then these can be generated to server/client side stubs and skeletons for you to add more.
Overview
IDL is a library used by all EOs to communicate efficiently across nodes. Using IDL, OpenClovis SAFplus Platform services can communicate across mixed endian machines and mixed mode (32-bit and 64-bit architecture) setup. This it accomplishes by providing marshalling and unmarshalling functions for the various types of arguments. Thus IDL in combination with RMD is used to provide a simple and efficient means of communication across EOs.
IDL Usage
The IDL generation is done through a script that takes 2 arguments:
- the xml file which provides a definition of the user’s EO and relevant data structures
- a directory in which to generate the code
Code is generated as follows:
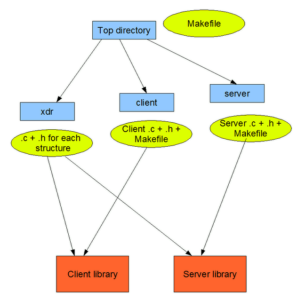
- Top level make file that recursively descends into client & server
- The directory xdr in which, a .c & .h is generated for every custom defined data structure in the xml.
For every structure, corresponding marshal.c and unmarshall.c files will be generated.
- client- a .c & .h is generated in this They contain the definition and declaration respectively of the sync client, async client and the async callback for each EO service defined in the xml. It also contains a make file that generates a library out of the files in this directory and the xdr directory.
- server – a .c & .h is generated in this directory. They contain the definition and declaration respectively of the server stub and the server function for each EO service defined in the It also contains a make file that generates a library out of the files in this directory and the xdr directory.
The generated code inside the target directory looks like the following:
IDL translates the user’s data structures passed through a function call to a message and vice versa. Therefore it requires the user to specify the function signatures. This is currently being done through xml. The user defines the EO through the xml along with the relevant data structures. The following section describes the xml definition in details.
IDL Specification
The IDL script expects the EO interface definition from the user in XML format.
User-defined datatypes
- Enumerations: like enum in C
- Structures: like structures in C
- Pointers
- length Var: required if the previous parameter is pointer
- Multiplicity: array datatype
- Unions: these are defined similar to The difference is in terms of the interpretation and generation.
EO Interface
The EO has multiple tables called Clients into which the exported interface functions are installed. The user has to specify which functions are installed in which tables and then give a declaration of the functions themselves. Thus, an EO interface definition consists of one or more clients
Marshalling and Unmarshalling
The IDL uses XDR to store data into a message. This is called marshalling of data. The reverse process i.e. of retrieving data from the message into the native format is called unmarshalling of data. XDR stands for eXternal Data Representation Standard (described in RFC 1832). It is a means of storing data in a machine independent format.
IDL Stubs
The IDL generates the following for every function installed in the EO interface:
- sync client stub
- async client stub
- server stub
- async callback
In addition, it generates 2 functions to install and uninstall the server functions into the EO.
A client function is defined by its arguments. Arguments or parameters are marshalled into a message which are passed to the server functions and vice versa. There 3 types of arguments: IN, OUT, INOUT. And an argument can be passed by value or by reference.
For more information how to create IDL and IDL stubs generation, please refer to chapter 11: Defining IDL of https://help.openclovis.com/index.php/Doc:latest/ideguide
Conclusion
IDL the way to define RMD methods. After IDL is created, a tool helps generate the IDL to IDL stubs for you to add more details. By this way, you can make RPC calls in OpenClovis SAFplus middleware environment.
Other support, please send email to support@openclovis.org.
