Introduction
YANG (Yet Another Next Generation) is a data modeling language used to model configuration data, state data, Remote Procedure Calls, and notifications for network management protocols. Developed as part of the IETF’s NETCONF standard, YANG allows developers to model data in a structured, hierarchical, and human-readable format. This language has become essential in modern network automation, enabling seamless interaction between devices and management systems. However, in the SAFplus the full potential of YANG is unlocked when it is combined with tools like Pyang to generate source code for specific programming languages, such as C++. In this article, we’ll explore how to use YANG models with Pyang to generate C++ source code, streamlining the process of integrating YANG-defined data models into your C++ applications.
YANG Models
YANG models describe the structure of configuration and state data in a hierarchical, tree-like format. Here are the blocks used to define the structure and organization of data:
- Container: A container is a complex data type that can hold other data nodes, such as leaf, leaf-list, or other container and list nodes. It is used to group related data elements together, providing a logical structure.
- List: A list is a collection of entries, where each entry is identified by a unique key. It can contain multiple instances of the same data structure. It is used to represent a collection of similar items.
- Leaf: A leaf is a single data element that holds a value of a specified type. It represents a basic data type and cannot contain other nodes. It is used to define individual attributes or properties of a data model.
- Leaf-list: A leaf-list is similar to a leaf, but it allows for multiple values of the same type. It represents a list of individual items. It is used when you want to allow multiple entries of the same data type, such as a list of IP addresses.
These constructs facilitate the creation of structured and organized data models in YANG, enabling effective network management and configuration.
Pyang
Pyang is a versatile YANG validator, parser, and translator written in Python. It allows users to validate YANG models, convert them into other formats, and even generate code in various programming languages. Pyang’s plugin architecture enables developers to extend its capabilities, including adding support for C++ code generation. Key features of Pyang include:
- Validation: Ensures that YANG models conform to the YANG standard.
- Translation: Converts YANG models into different formats, such as XML, JSON, or source code.
- Extensibility: Supports custom plugins to extend functionality, including code generation for various languages.
- Ease of Use: Offers a command-line interface with clear options for generating outputs.
- Error Reporting:Provides detailed error messages to help debug issues in YANG models.
Example Generating C++ Code from YANG Models in SAFplus
To illustrate YANG’s capabilities, consider the following steps:
- Prepare the YANG Model

- module network: This is the main identifier for the YANG data model, encapsulating all contained definitions.
- container ethernet: This section groups relevant data related to Ethernet interfaces. The use of a container helps organize the data logically.
- list interfaces: This defines a collection of Ethernet interfaces, allowing multiple entries, each uniquely identified by the key ename.
- key “ename”: This specifies that each entry in the list is identified by the ename leaf, which represents the name of the interface. This ensures uniqueness within the list.
- leaf: represents an attribute of an Ethernet interface with the basic type.
- rpc get_interface: This defines a remote procedure call that allows external entities to request data about a specific interface.
- notification AddressFailover: This defines an event notification that can be sent when an IP address fails over.
- Run Pyang with the C++ Plugin
pyang -f y2cpp network.yang --y2cpp-output <output directory> --y2cpp-mgt
<location of management framework>
- -f y2cpp: This flag specifies the output format. In this case, y2cpp indicates that the output should be generated in C++ format.
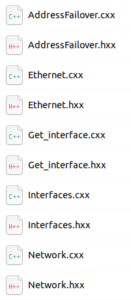
- Result
Here are the files generated that include: C++ Classes, Member Variables, Getters and Setters, RPC Method Implementation, Notification Handling, Serialization and Deserialization, Error Handling, etc
Advantages of Combining YANG, Pyang, and C++
- Automation:Automates the process of creating C++ classes from YANG models.
- Consistency:Ensures consistency between the data model and the implementation.
- Interoperability:Simplifies integration with NETCONF or RESTCONF-based systems.
- Scalability:Supports large-scale network configurations through structured code.
Conclusion
The combination of YANG, Pyang, and C++ is a powerful solution for developers working on large systems. By automating the generation of C++ code from YANG models, Pyang reduces the potential for errors and speeds up development. With these tools, you can seamlessly incorporate YANG-defined data structures into your C++ applications, enhancing both productivity and reliability.
Other support, please send email to support@openclovis.org.
